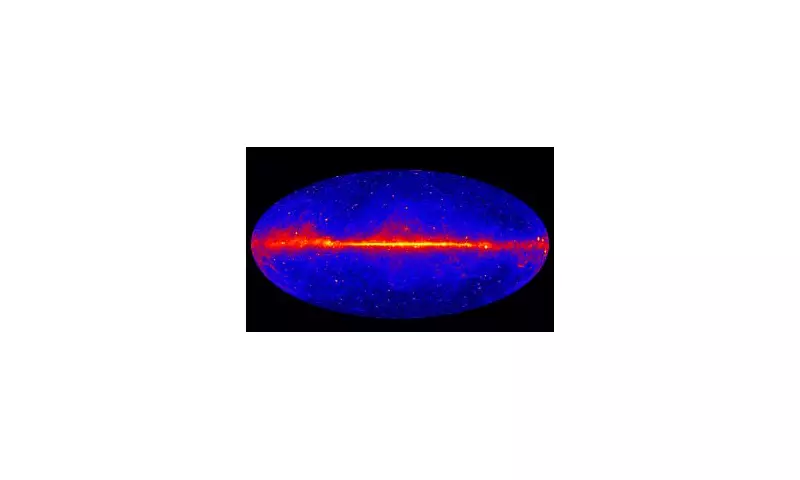
In a monumental breakthrough that could fundamentally alter our understanding of the cosmos, scientists believe they have captured the first photographic evidence of dark matter - the mysterious substance that makes up 85% of the universe yet has remained invisible to detection until now.
The Cosmic Detective Story
Researchers have spent decades hunting for direct evidence of dark matter, which doesn't emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it notoriously difficult to observe. The international team, led by Dr. Mike Wilkes from the University of Aberdeen, has developed an innovative approach that may have finally cracked this cosmic mystery.
How They Saw the Invisible
Using sophisticated computer simulations and gravitational lensing techniques, the scientists created what they describe as a "dark matter template" - a method that allows them to indirectly observe the elusive substance through its gravitational effects on visible matter.
The key findings include:
- Dark matter forms an intricate cosmic web connecting galaxies
- This invisible scaffolding dictates the large-scale structure of the universe
- The discovery confirms theoretical predictions about dark matter distribution
- Previous detection methods using particle colliders have failed to provide direct evidence
Why This Changes Everything
This photographic evidence represents more than just a scientific curiosity. Dark matter is the fundamental building block of our universe, responsible for holding galaxies together and governing cosmic evolution. Without its gravitational influence, galaxies would fly apart, and the universe as we know it wouldn't exist.
Dr. Wilkes explained the significance: "For the first time, we're not just inferring dark matter's presence through mathematical equations - we're seeing its structure and how it shapes the visible universe around us."
The Future of Cosmic Exploration
This breakthrough opens new frontiers in astrophysics and could lead to:
- New understanding of galaxy formation and evolution
- Advanced dark matter mapping techniques
- Potential applications in gravitational physics
- New directions for the search for dark matter particles
The research team emphasizes that while this represents compelling evidence, further verification and refinement of their techniques will be necessary. However, the scientific community is already hailing this as a potential Nobel Prize-worthy discovery that brings us one step closer to understanding the true nature of our universe.





