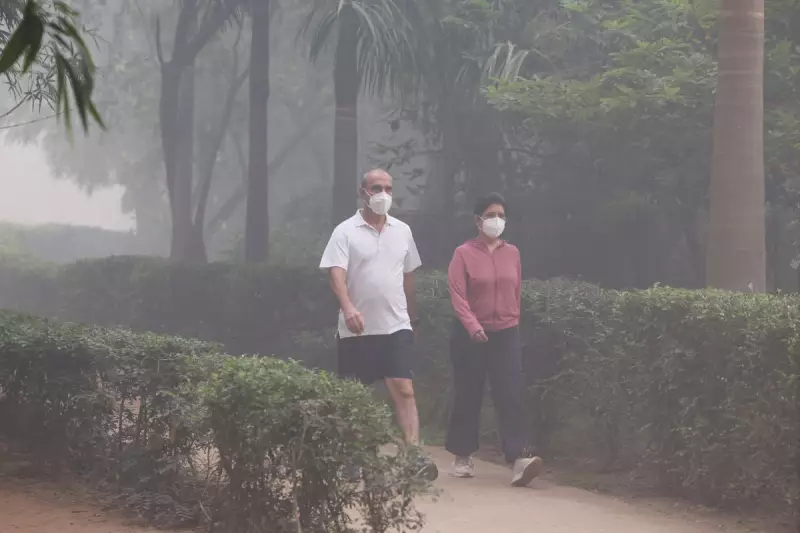
Authorities in India's capital are preparing an ambitious technological intervention to battle the relentless heatwave scorching Delhi. The city government has given preliminary approval for a cloud seeding project aimed at artificially inducing rainfall to provide much-needed relief from soaring temperatures and hazardous pollution levels.
The Science Behind Artificial Rain
Cloud seeding involves dispersing substances like silver iodide or salt particles into clouds to encourage precipitation. The technique, which has been used in various countries including China and the UAE, works by providing nuclei around which water vapour can condense, ultimately forming rain droplets.
Delhi's plan comes as the city grapples with temperatures consistently exceeding 40°C and air quality that frequently dips into the 'very poor' category. The extreme conditions have raised serious health concerns among the city's 20 million residents.
A Race Against Time and Weather
The project faces significant logistical challenges, with officials acknowledging they need to act before the natural monsoon season arrives in late June or early July. The Delhi government has engaged scientists from the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, who have been researching cloud seeding possibilities since 2018.
Critical factors for success include:
- Availability of moisture-bearing clouds at the right altitude
- Favorable wind patterns and atmospheric conditions
- Coordination with aviation authorities for aircraft deployment
- Timely execution before monsoon clouds gather
Environmental Impact and Cost Considerations
While the potential benefits are clear, environmental scientists are urging caution. The long-term ecological effects of cloud seeding remain incompletely understood, and the project carries a substantial price tag of approximately 1 million rupees per operation.
The Delhi government views this as a necessary investment in public health and environmental management. If successful, the initiative could provide a blueprint for other Indian cities struggling with similar climate challenges.
As Delhi awaits either artificial or natural relief, residents continue to endure the dual burden of extreme heat and poor air quality, highlighting the urgent need for innovative solutions to urban climate crises.