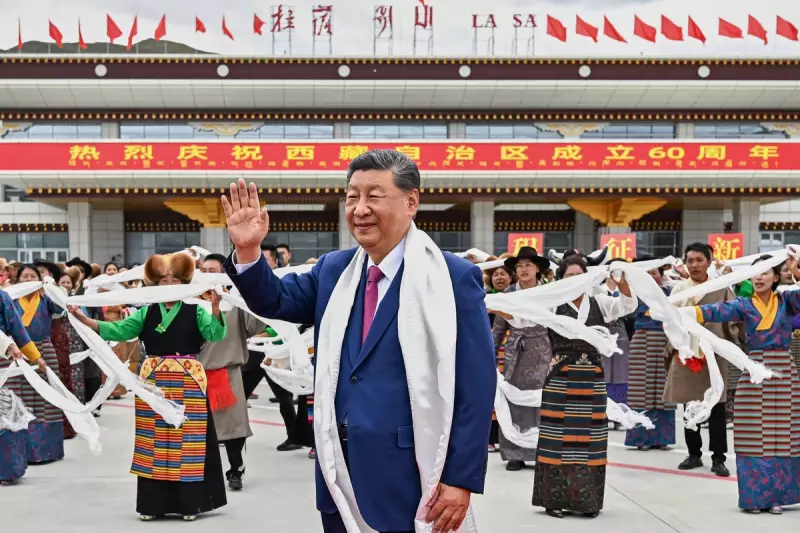
Chinese President Xi Jinping has made a highly significant official visit to Tibet, marking his first publicised trip to the autonomous region since assuming power. The journey underscores Beijing's enduring focus on stability and development in the strategically vital Himalayan territory.
During his tour, President Xi stressed the critical importance of ethnic unity and social stability. He called for sustained efforts to ensure all ethnic groups in Tibet work together for continued peace and prosperity, a long-standing priority for the Chinese government.
Focus on Development and Infrastructure
A central theme of Xi's visit was the commitment to Tibet's comprehensive development. He emphasised ambitious plans to transform the region into a 'beautiful, prosperous, and civilised' area, aligning with broader national goals for modernisation.
The Chinese leadership views infrastructure and economic projects as key to integrating Tibet more fully into the nation's framework. This includes enhancing transport links, boosting tourism, and improving living standards for its residents.
A Rare and Symbolic Gesture
Presidential visits to Tibet are infrequent and carry substantial symbolic weight. Xi's presence in Lhasa, the regional capital, sends a powerful message of Beijing's authority and its unwavering commitment to the region it has administered for decades.
The trip is widely seen as a move to reinforce national policies in Tibet and demonstrate the central government's active engagement in its affairs, from economic planning to social governance.
The Broader Context
Tibet remains a topic of international discussion, with various perspectives on its history and governance. China consistently asserts its sovereignty over the region and points to developmental achievements and improved infrastructure as evidence of successful policy.
President Xi's visit serves to highlight these narratives, focusing on themes of progress, unity, and a future vision for Tibet under Chinese administration, while indirectly addressing external viewpoints.