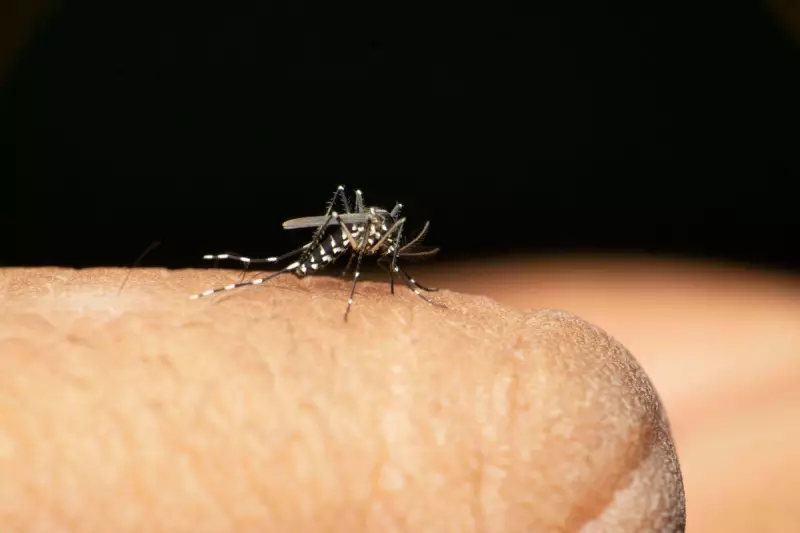
Health officials in England are on high alert after confirmed sightings of the invasive Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) in southern regions. This aggressive species, native to Southeast Asia, is a known carrier of dangerous tropical diseases including dengue fever, Zika virus and chikungunya.
Why This Matters
The discovery marks a significant expansion of the mosquito's territory into northern Europe, with climate change creating warmer conditions that allow these insects to thrive. Unlike native UK mosquitoes that mainly feed at dusk, the Asian tiger mosquito bites aggressively throughout daylight hours.
Public Health Risks
While no local transmissions have been reported yet, experts warn the presence of this vector species increases the risk of:
- Dengue fever outbreaks
- Zika virus transmission
- Chikungunya infections
- Yellow fever potential
What Authorities Are Doing
The UK Health Security Agency has implemented enhanced surveillance measures, including:
- Setting up additional mosquito traps in high-risk areas
- Training local health teams in identification
- Developing contingency plans for potential outbreaks
Residents are advised to eliminate standing water where mosquitoes breed and report unusual biting activity to local health authorities.
Climate Connection
Entomologists attribute this spread to warming temperatures across Europe. "What was once a tropical species can now survive winters in southern England," warned Dr. Sarah Jeffries of the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology. "This is exactly the type of public health impact we predicted from climate change."