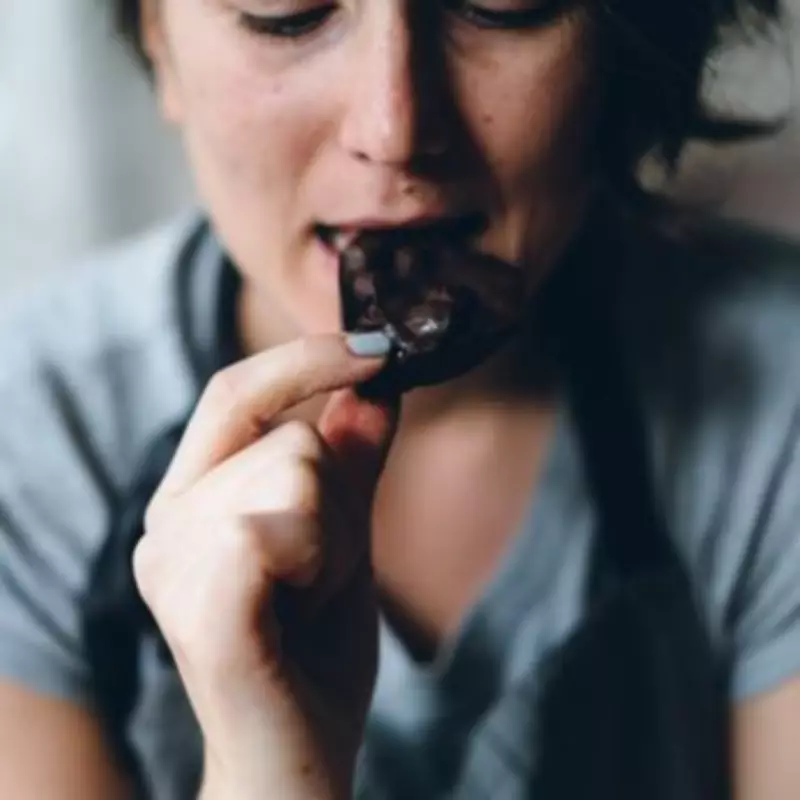
New research suggests that incorporating dark chocolate into your diet could offer significant cardiovascular benefits, but experts emphasise that strict moderation is crucial to avoid potential health drawbacks.
The Science Behind Chocolate's Health Properties
Nutrition specialists have identified dark chocolate as a potentially beneficial food for heart health, primarily due to its elevated cocoa content compared to milk or white varieties. This higher concentration of cocoa unlocks specific advantages through naturally occurring plant compounds called flavanols.
Understanding Flavanols and Their Effects
Dell Stanford, a qualified nutritionist with fifteen years of experience, explained to the British Heart Foundation that "flavanols give dark chocolate its slightly bitter taste, and its potential health benefits, such as helping to lower blood pressure and making blood vessels more flexible."
These compounds are responsible for dark chocolate's characteristic sharp flavour and are believed to improve blood circulation throughout the body by enhancing vascular flexibility.
The Precise Recommended Amount
Research indicates that consuming approximately 45 grams of dark chocolate weekly – equivalent to two to four modest squares – correlates with the most significant reduction in cardiovascular risk. This finding emerged from a comprehensive 2019 review of observational studies examining chocolate consumption patterns.
Stanford highlighted that maintaining this balance is essential, as exceeding this amount could trigger adverse health consequences due to excessive sugar and calorie intake.
Why Moderation Matters
Despite its potential benefits, dark chocolate contains substantial calories, fat, and sugar that can outweigh advantages when consumed excessively. The fat in dark chocolate primarily comes from cocoa butter, which comprises 50 to 60 percent saturated fat.
Regular overindulgence can increase levels of 'bad' non-HDL cholesterol and contribute to weight gain, potentially negating any cardiovascular benefits.
Important Considerations and Warnings
Nutrition experts stress that dark chocolate isn't suitable for everyone and comes with several important caveats:
- Caffeine content: Dark chocolate contains caffeine that must be factored into daily limits – particularly crucial for pregnant women whose allowance drops to approximately 200mg
- Allergy risks: Some individuals may have allergic reactions to components including milk, soy, nuts, or gluten
- Heavy metal concerns: Many dark chocolate bars contain significant levels of lead and cadmium, which can accumulate in the body and potentially cause kidney damage, hypertension, and immune system suppression
- Processing matters: Genuine benefits stem from minimally processed, high-cocoa chocolate rather than sugar-laden commercial varieties
The Reality of Achieving Benefits
During a recent Radio 4 podcast discussion, experts revealed a surprising reality about obtaining sufficient flavanols from chocolate. One specialist explained that while possible, "you'd have to eat about four times the daily energy allowance for an adult. You would eat about 10,000kcal a day" to achieve meaningful flavanol intake from chocolate alone.
This highlights why dark chocolate should be viewed as a potential supplement to a balanced diet rather than a primary source of health benefits.
Balancing Enjoyment with Health Consciousness
The research presents a nuanced picture: while dark chocolate consumption in specific, limited quantities may contribute to reduced cardiovascular risks, it requires careful portion control and awareness of individual health circumstances.
Nutrition professionals recommend focusing on high-quality, minimally processed dark chocolate with maximum cocoa content when choosing to incorporate it into your diet, while remaining mindful of overall calorie and sugar intake from all sources.