NHS Issues Critical Alert on Common Blood Pressure Medication
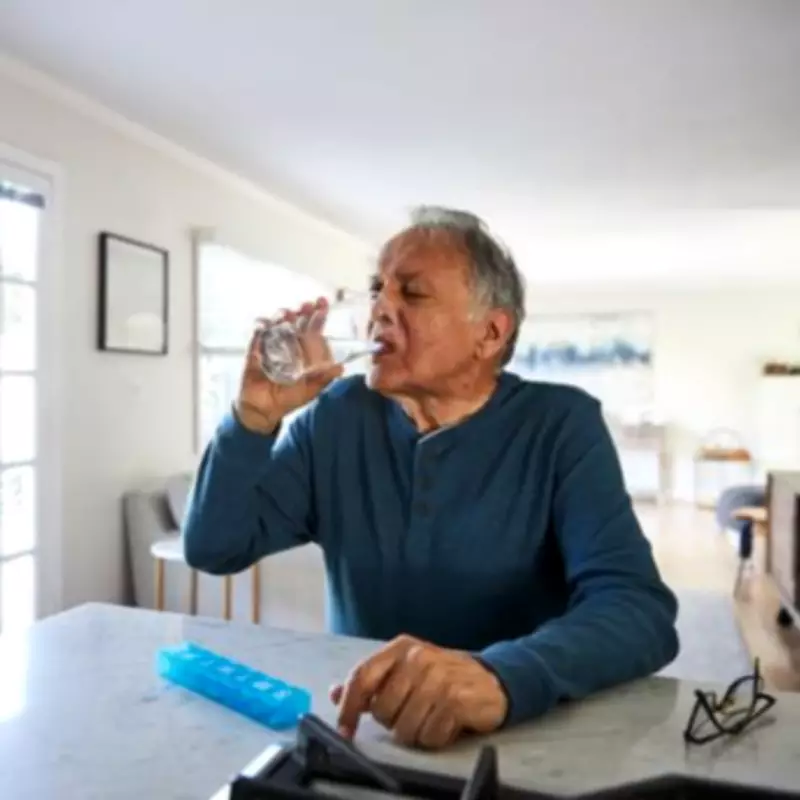
The National Health Service has issued a significant safety alert concerning furosemide, a widely prescribed diuretic medication used by millions across the United Kingdom to manage conditions including heart failure and hypertension. This crucial guidance comes as the medication was dispensed approximately 11 million times throughout 2024, highlighting its extensive use across all age demographics from paediatric patients to elderly individuals.
Eight Specific Patient Groups Requiring Immediate GP Consultation
The NHS has explicitly identified eight distinct patient categories who must arrange a consultation with their general practitioner before commencing furosemide treatment to ensure their safety. This precautionary measure is essential for preventing potential adverse reactions and complications associated with this commonly prescribed medication.
The NHS advises that the following individuals must speak with their doctor before taking furosemide:
- Anyone who has previously experienced an allergic reaction to furosemide or any other medication
- Individuals currently experiencing low blood pressure (medically known as hypotension)
- Patients displaying signs of dehydration, including persistent thirst, dry mouth, or dark-coloured urine
- Those diagnosed with any form of liver disease
- Patients with a diabetes diagnosis
- Individuals experiencing difficulties with urination
- Patients diagnosed with Addison's disease, a rare disorder affecting the adrenal glands
- Individuals with a gout diagnosis
Additional Medical Scenarios Requiring Professional Advice
Beyond these eight specific groups, the NHS further recommends that furosemide users consult their healthcare provider in several additional medical situations. These include patients scheduled for glucose testing, those undergoing procedures involving iodine-based dye injections for X-rays or scans, and individuals preparing for major surgical operations requiring general anaesthesia.
The NHS clarifies that "diuretics are sometimes called 'water tablets' because they make you pee more. This helps get rid of extra fluid in your body." Furosemide remains a prescription-only medication available in tablet and liquid formulations for oral administration, with injectable forms typically reserved for hospital settings.
Critical Medication Interactions and Safety Precautions
Patients prescribed furosemide must exercise particular caution regarding potential drug interactions, as certain medications can either diminish its effectiveness or amplify side effects. This warning extends to common over-the-counter remedies including paracetamol, co-codamol, and various heartburn and indigestion treatments.
The NHS specifically advises consulting a doctor before combining furosemide with:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as diclofenac, ibuprofen, or naproxen
- Medications affecting blood potassium levels, including potassium supplements, steroids, or other diuretics
- Drugs treating irregular heart rhythms, including amiodarone, digoxin, disopyramide, flecainide, or sotalol
- Soluble formulations of paracetamol and co-codamol
- Specific heartburn and indigestion remedies
- Mental health medications including amisulpride, lithium, pimozide, or risperidone
- Blood pressure medications or drugs with hypotensive side effects
- The ulcer treatment sucralfate, requiring a two-hour separation from furosemide dosing
The NHS emphasises: "Tell your doctor if you are taking any potassium supplements. These change the levels of potassium in your blood and can affect the way furosemide works." Regarding herbal remedies and supplements, the health service notes insufficient safety data, as these products undergo different testing protocols than pharmaceutical medications and are rarely evaluated for interaction potential.