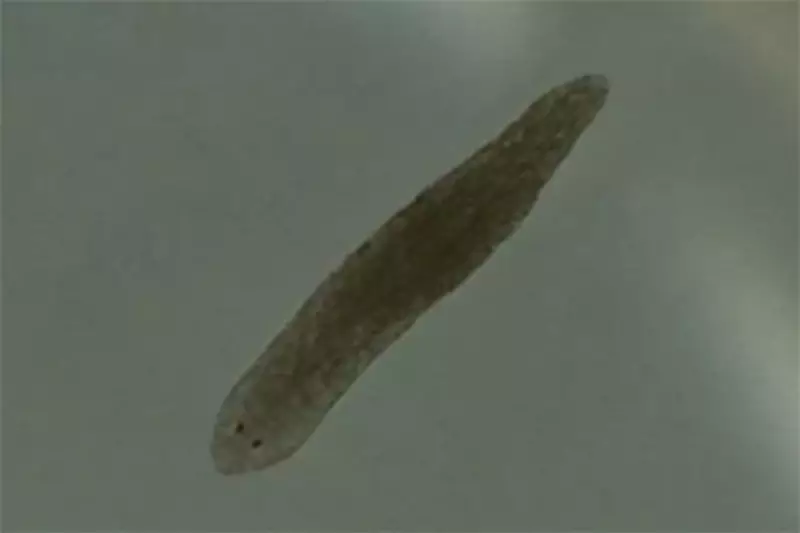
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have found that tiny flatworms, known as planarians, may unlock new treatments for schizophrenia and drug addiction. These creatures share surprising genetic similarities with humans, making them ideal for neurological research.
Why Planarians?
Planarians possess a remarkable ability to regenerate, but more importantly, their nervous systems respond to psychoactive substances in ways comparable to humans. Researchers believe studying these worms could lead to breakthroughs in understanding mental health disorders.
Key Findings
- Planarians react to drugs like amphetamines and cocaine similarly to humans.
- Their genetic makeup includes dopamine receptors, which play a crucial role in addiction and schizophrenia.
- Studying their regenerative abilities could help repair brain damage caused by substance abuse.
Potential for Future Treatments
This research opens doors to developing targeted therapies for addiction and mental illness. By analysing how these worms process dopamine, scientists hope to create drugs with fewer side effects.
"Planarians offer a simple yet powerful model for studying complex human conditions," said one researcher. "Their biology could revolutionise psychiatric medicine."