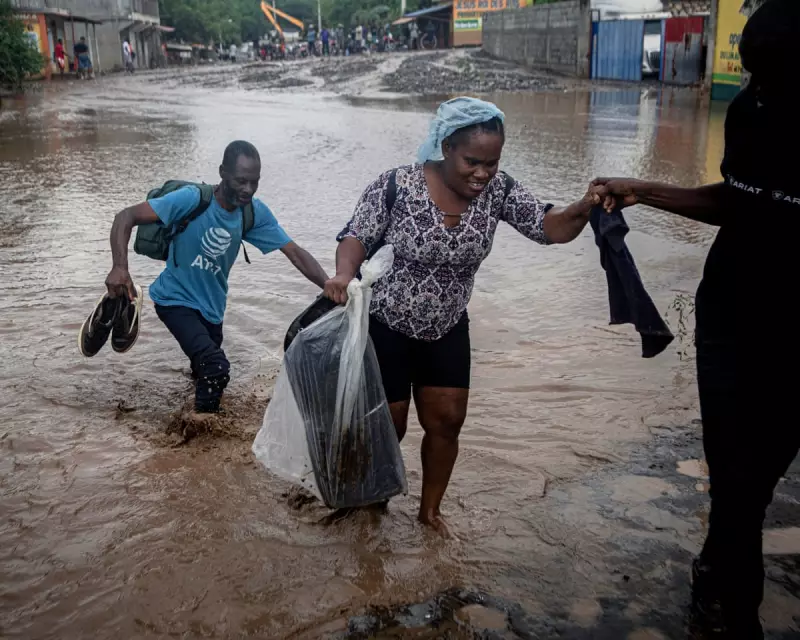
A powerful and dangerous hurricane is carving a destructive path through the Caribbean, with forecasters warning of potentially catastrophic consequences for several island nations. Hurricane Melissa has rapidly intensified into a Category 4 storm, packing sustained winds of 130mph and threatening Jamaica, Haiti, and eastern Cuba with extreme weather conditions.
Storm Intensification Reaches Critical Levels
Meteorologists are reporting that Melissa has undergone significant strengthening, transforming from a tropical storm into a major hurricane within a remarkably short timeframe. The storm's rapid intensification has caught the attention of weather experts worldwide, who note the unusually warm Caribbean waters are providing ideal conditions for the hurricane's development.
Emergency Preparations Underway Across Caribbean
Emergency response teams across the region are working against the clock as Hurricane Melissa approaches. In Jamaica, authorities have initiated evacuation protocols for coastal and low-lying areas, while Haiti's disaster management agency has activated emergency operations centres. Cuban meteorological services are closely monitoring the storm's trajectory, with particular concern for eastern provinces.
Projected Impact and Immediate Threats
The Weather Tracker analysis indicates several critical threats from Hurricane Melissa:
- Destructive Winds: Sustained hurricane-force winds exceeding 130mph capable of severe structural damage
- Storm Surge: Life-threatening coastal flooding with water levels rising up to 12 feet above normal tide levels
- Torrential Rainfall: Widespread precipitation of 8-12 inches, with isolated areas potentially receiving up to 20 inches
- Flash Flooding: Significant risk of devastating flash floods and mudslides, particularly in mountainous regions
Regional Weather Patterns and Broader Implications
Beyond the immediate hurricane threat, weather systems across the Atlantic are showing unusual activity. A separate low-pressure system is developing east of Bermuda, though forecasters currently assess its direct threat to land as minimal. Meanwhile, southern Europe braces for severe weather of its own, with heavy rainfall and potential flooding expected across Mediterranean regions.
The convergence of these weather events highlights the increasingly volatile nature of global weather patterns, with climate scientists noting connections to broader environmental changes affecting storm intensity and frequency in tropical regions.