Health authorities in Tennessee have declared a significant outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD), urging parents and caregivers to remain vigilant as the highly contagious virus spreads through communities.
What is Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease?
HFMD is a common childhood illness caused by viruses from the Enterovirus family, particularly coxsackievirus. While typically affecting young children, adults can also contract the virus, making this outbreak a concern for entire families.
Recognising the Symptoms
The disease manifests through several distinctive symptoms that parents should watch for:
- Fever and reduced appetite: Often the first signs to appear
- Painful mouth sores: These can make eating and drinking difficult
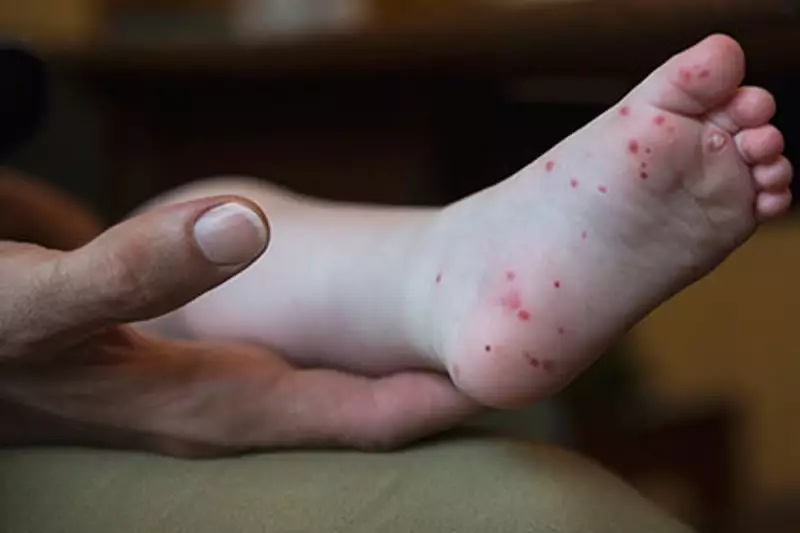
- Skin rash with blisters: Typically appears on palms of hands and soles of feet
- Sore throat and general malaise: Accompanying flu-like symptoms
How the Virus Spreads
HFMD transmits easily through multiple routes, contributing to rapid community spread:
Person-to-person contact: The virus travels through close personal interaction, coughing, sneezing, and contact with contaminated surfaces. It can also spread via contact with faeces, making proper hygiene crucial in childcare settings.
Prevention and Management
While there's no specific treatment for HFMD, health officials recommend several preventive measures:
- Frequent handwashing: Use soap and water consistently
- Surface disinfection: Regularly clean toys and common areas
- Avoid close contact: Keep infected children home from school
- Symptom management: Use over-the-counter pain relievers and ensure adequate fluid intake
Most cases resolve within 7-10 days without complications, though medical attention may be necessary if symptoms worsen or dehydration occurs.
Tennessee health departments are monitoring the situation closely and will provide updates as the outbreak develops.





