Health officials are alerting parents to a seasonal increase in cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), a common viral infection affecting young children. The illness, which typically peaks in summer, is expected to surge in the coming weeks.
What is Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
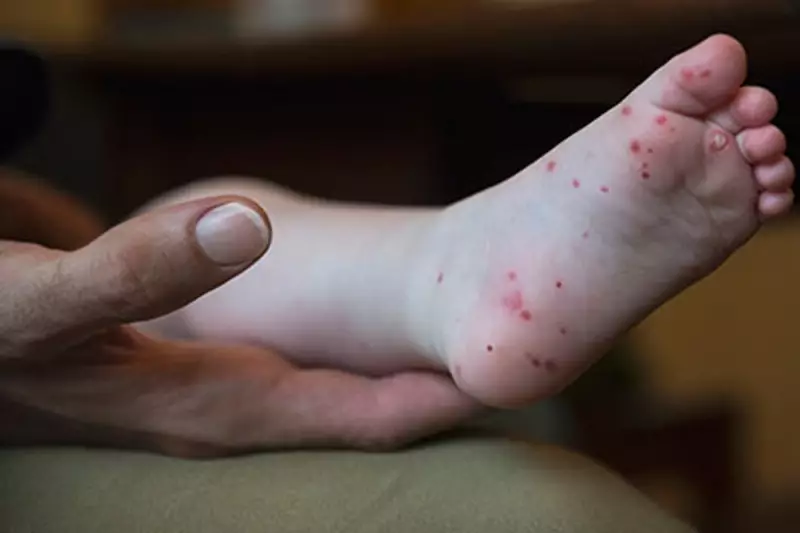
HFMD is a contagious viral infection caused by the Coxsackievirus. It primarily affects children under 10, though adults can occasionally contract it. Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Painful mouth ulcers
- A rash on hands and feet
Why Summer Brings More Cases
The virus thrives in warm weather and spreads easily in settings where children gather, such as:
- Nurseries
- Playgroups
- Swimming pools
"Summer activities and closer contact between children create ideal conditions for transmission," explains Dr. Sarah Jennings, a paediatric infectious disease specialist.
Prevention and Treatment
While HFMD is usually mild, parents should:
- Encourage frequent handwashing
- Disinfect shared toys
- Keep infected children home until symptoms subside
Most cases resolve within 7-10 days without medical treatment. However, parents should seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or if their child shows signs of dehydration.
The NHS recommends using paracetamol for fever and ensuring children stay hydrated. There is no vaccine currently available for HFMD in the UK.