Entertainment
Holly Willoughby Revives Modelling Era in Reformation Campaign
Holly Willoughby showcases a youthful new look with longer blonde hair in a Reformation fashion campaign, reminiscent of her early modelling days before television fame.
Sports
World Cup 2026 Ticket Frenzy Defies High Costs and Global Tensions
With 100 days until the 2026 World Cup in North America, unprecedented ticket demand clashes with staggering prices and geopolitical anxieties, including US-Iran tensions and immigration concerns.
Politics
Israel Strikes Iran's Presidential Office as US Embassy in Oman Issues Shelter Alert
Israeli airstrikes target Iran's Presidential Office and Supreme National Security Council in Tehran, with US embassy staff in Oman told to seek cover amid escalating Middle East conflict.
Crime
Sarah Everard's Mother Pens Heartfelt Tribute Five Years After Murder
Susan Everard remembers her daughter Sarah in British Vogue, describing her as someone who 'added to the beauty of the world' through her travels, dancing, and strong moral compass.
Business
Health
Weather
Sunshine Brings Pollen Bomb to UK After Weeks of Rain
After over 50 days of consecutive rain, the UK is basking in sunshine with temperatures reaching 19°C, but the warm weather has triggered a severe 'pollen bomb' across the nation.
Maldives Easter Flight Prices Skyrocket Amid Middle East Airport Shutdowns
Holidaymakers face soaring costs for direct flights to the Maldives this Easter, with prices exceeding £2,500, as Middle East airport closures disrupt travel routes and drive up fares.
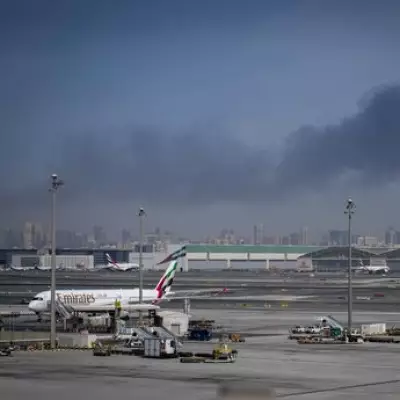
Middle East Airspace Crisis Strands Britons, Airlines Scramble
Widespread airspace closures across the Middle East due to escalating Iran-US tensions have caused major flight disruptions, leaving British nationals stranded and airlines operating limited repatriation services.
Turkey Travel Safety: FCDO Advice Amid Conflict
The UK Foreign Office updates travel advice for Turkey as Middle East tensions escalate. Flights face cancellations, but most trips remain unaffected unless near the Syrian border.
Record Winter Rainfall Hits Three English Counties
Cornwall, Leicestershire, and West Midlands experience wettest winter on record, with southern England seeing fourth wettest. Met Office links heavy downpours to climate change impacts.
Tech
Get Updates
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox!
We hate spammers and never send spam
Environment
Monday Sports Challenge: Football, Cricket & Rugby Questions
Start your week with our Monday sports quiz featuring 100 questions about British football, cricket, and rugby. How well do you know these popular UK sports?