New research offers promising evidence that a targeted dietary approach, rich in specific vegetables and beneficial bacteria, could help slow the progression of a common form of cancer in men.
Study reveals powerful combination
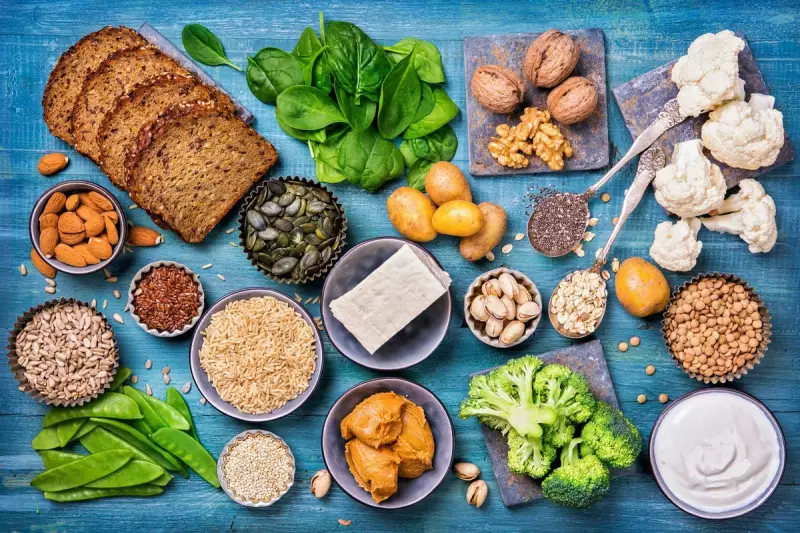
A scientific trial has investigated the impact of a novel supplement combined with a probiotic on men diagnosed with low-risk prostate cancer. The supplement was developed from a blend of food-derived ingredients, including broccoli, turmeric, and green tea. This was paired with a specific strain of Lactobacillus probiotic.
The study, which involved 212 men, yielded highly encouraging results. Researchers reported that over 90% of the participants who took the combined supplement and probiotic experienced either a regression of their disease or a stabilisation, meaning the cancer did not advance.
Measurable health benefits beyond cancer markers
The positive effects of the intervention were measured in several key areas. Most notably, it significantly slowed the progression of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a critical marker monitored in prostate cancer patients.
Beyond the primary cancer-related metrics, men in the trial also reported improvements in other aspects of their health. These included:
- Reduced urinary symptoms
- Decreased levels of inflammation
- Enhanced physical strength
A note of caution and the path forward
While the initial findings, reported on Wednesday 7 January 2026, are undoubtedly positive, scientists emphasise the need for longer-term research. The crucial question remains whether these dietary strategies can reliably reduce the need for major medical interventions, such as surgery or radiotherapy, over an extended period.
This study adds to a growing body of evidence highlighting the powerful role nutrition can play in managing health conditions. It provides a tangible, research-backed dietary hack for men seeking to actively manage low-risk prostate cancer alongside conventional medical guidance.