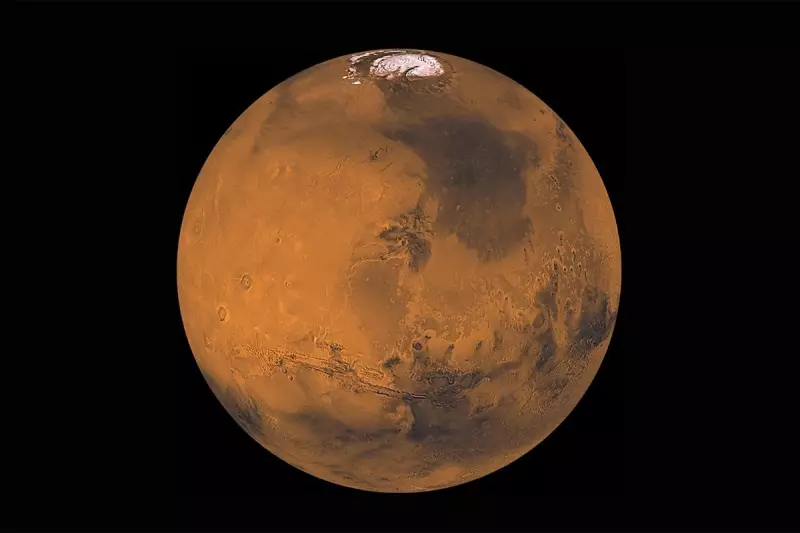
In a discovery that has left planetary scientists both intrigued and perplexed, data from NASA's now-retired InSight lander has revealed the presence of massive, unexplained subterranean 'blobs' of molten rock deep beneath the Martian surface.
The findings, which stem from the most comprehensive analysis of seismic data ever conducted on another planet, fundamentally challenge long-held beliefs about the geological inactivity and cold, dead interior of Mars.
A Mission of Firsts Uncovers a Mystery
Stationed on the vast, flat plains of Elysium Planitia, the InSight lander (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) spent four years listening to the heartbeat of Mars. Its primary tool, a supremely sensitive seismometer, detected over 1,300 marsquakes, painting a detailed picture of the planet's inner structure for the very first time.
While scientists expected to find clues about the planet's formation, they did not anticipate the scale of the mystery that lay in wait.
The Puzzling Subsurface Anomalies
The seismic waves revealed two colossal anomalies roughly 100 kilometres beneath the surface. Analysis indicates these structures are not solid rock but are instead composed of a molten, or partially molten, material—a substance hot enough to slow down the seismic waves passing through them.
This presence of such extensive magma is utterly confounding. The prevailing scientific consensus has long been that Mars is a largely geologically dead world, its volcanic fury spent billions of years ago. The discovery of these massive molten blobs suggests its interior is far more dynamic and complex than anyone imagined.
Rethinking the Red Planet's History
This revelation forces a dramatic rethink of Martian geological history and thermal evolution. The existence of this magma implies a significant heat source is still present within the planet's interior, a fact that current models struggle to explain.
Scientists are now grappling with several profound questions:
- What is the true source of heat keeping this material molten?
- Could this magma find a way to the surface, potentially leading to future volcanic activity?
- How does this finding change our understanding of how rocky planets like Mars cool and evolve over billions of years?
The findings cement the legacy of the InSight mission, proving that even a 'dead' planet can hide vibrant secrets. The quest to understand these mysterious Martian blobs has only just begun, promising to unlock new chapters in the story of our solar system.