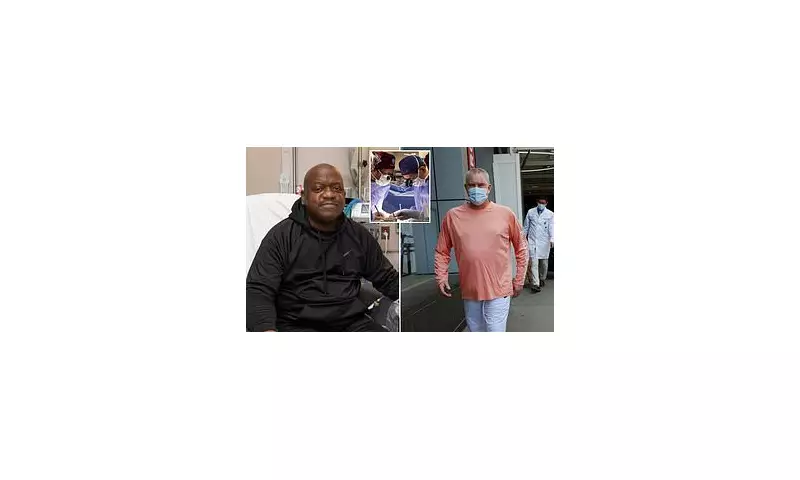
In a revolutionary medical breakthrough that could transform transplant medicine, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted landmark approval for clinical trials involving the transplantation of genetically modified pig organs into human patients.
This pioneering decision marks a significant step toward addressing the critical shortage of donor organs that leaves thousands of British patients on lengthy waiting lists each year. The technology could potentially save countless lives by providing a sustainable alternative to human organ donation.
The Science Behind Xenotransplantation
Researchers have developed sophisticated genetic modification techniques that alter pig organs to make them compatible with human biology. These modifications prevent immediate rejection by the human immune system, which has been the primary obstacle in previous cross-species transplantation attempts.
The genetically engineered pigs are raised in sterile, controlled environments to ensure they are free from viruses and pathogens that could potentially transfer to human recipients.
Potential Impact on UK Healthcare
For the NHS and British patients, this development offers tremendous hope. Currently, over 6,000 people are waiting for organ transplants in the UK, with many facing years of uncertainty and deteriorating health while on waiting lists.
Professor Sarah Wilkinson, a leading transplant specialist at Cambridge University Hospitals, commented: "This approval represents the most significant advancement in transplant medicine in decades. While there are still challenges to overcome, the potential to eliminate organ waiting lists is now within sight."
Ethical Considerations and Safety Protocols
The clinical trials will follow rigorous ethical guidelines and safety protocols. Initial procedures will focus on patients who have exhausted all other treatment options and who provide fully informed consent regarding the experimental nature of the treatment.
Regulatory bodies will maintain strict oversight throughout the trial process, monitoring patients for any adverse reactions or long-term complications.
Medical ethicists emphasize the importance of balancing innovation with patient safety, ensuring that desperate patients are not exposed to unnecessary risks despite the potential benefits.
Future Implications
If successful, this technology could eventually expand beyond life-saving organ transplants to include other medical applications such as pancreatic islet cells for diabetes treatment or neurological tissues for degenerative conditions.
The UK medical research community is closely monitoring these developments, with several British institutions preparing to participate in international research collaborations related to xenotransplantation technology.
While widespread availability remains several years away, this FDA approval represents a crucial milestone toward making organ transplantation accessible to all who need it, potentially ending the tragic reality of patients dying while awaiting suitable donors.